Следующая задача 407. Trapping Rain Water II даёт возможность потренировать пространственное воображение (по крайней мере на этапе выбора адекватного для её решения алгоритма).
📋 Описание задачи
Дана 3D-сетка, представляющая высоты ячеек. Необходимо вычислить объем воды, который можно удержать после дождя. Вода может заполнять только области, окруженные ячейками с большей высотой.
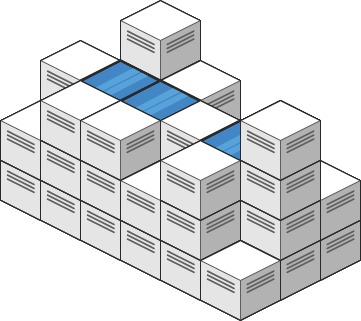
💡 Идея
Мы рассматриваем каждую ячейку как часть сетки, где вода может стекать только в соседние ячейки с меньшей или равной высотой. Используя структуру данных непересекающихся множеств (Disjoint-Set или Union-Find), мы группируем соединённые ячейки и отслеживаем их связь с границами, чтобы определить, какие ячейки могут удерживать воду.
🛠️ Детали подхода
-
Представление и сортировка:
- Преобразуем все ячейки в список, где каждая ячейка представлена своей высотой и координатами.
- Сортируем ячейки по высоте в порядке возрастания.
-
Структура объединения множеств:
- Создаем дискретное множество для ячеек, добавляя виртуальный узел для границ сетки.
- На каждом шаге объединяем текущую ячейку с её соседями, если их высота меньше или равна текущей.
-
Вычисление объема воды:
- Для каждой высоты подсчитываем количество внутренних ячеек, не связанных с границами.
- Умножаем разницу высот на число таких ячеек и добавляем результат к общему объему воды.
📈 Асимптотика
-
Временная сложность:
- Сортировка ячеек:
O(m × n × log(m × n)).
- Операции Disjoint-Set:
O(m × n × α(m × n)), где α — обратная функция Аккермана.
- Итог:
O(m × n × log(m × n)) (доминирует сортировка).
-
Пространственная сложность:
- Структура объединения множеств:
O(m × n).
- Дополнительная память для хранения списка ячеек:
O(m × n).
- Итог:
O(m × n).
📜 Исходный код
struct DisjointSet {
parent: Vec<usize>,
size: Vec<usize>,
}
impl Solution {
// Directions for moving up, down, left, and right
const directions: [(i32, i32); 4] = [(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1)];
pub fn trap_rain_water(height_map: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let m = height_map.len();
let n = height_map[0].len();
// Handle edge cases: if the grid is too small to trap water, return 0
if m < 3 || n < 3 {
return 0;
}
// Helper function to map a cell's row and column to a unique index in the disjoint set
let cell_index = |r: usize, c: usize| -> usize { 1 + r * n + c };
// Helper function to validate a neighbor cell and convert it to its grid coordinates
let to_valid_cell = |r: i32, c: i32| -> Option<(usize, usize)> {
if (0..m as i32).contains(&r) && (0..n as i32).contains(&c) {
Some((r as usize, c as usize))
} else {
None
}
};
// Helper function to check if a cell is on the boundary of the grid
let is_boundary_cell = |r: usize, c: usize| r == 0 || r == m - 1 || c == 0 || c == n - 1;
// Flatten the grid into a list of cells with their heights and coordinates
let mut cells = Vec::new();
for r in 0..m {
for c in 0..n {
cells.push((height_map[r][c], r, c));
}
}
// Sort the cells by height in ascending order
cells.sort_by_key(|&(h, _, _)| h);
// Initialize the disjoint set with an extra node for the boundary
let mut ds = DisjointSet::new(m * n + 1);
let boundary = 0; // Special index representing the boundary node
let mut volume = 0; // Total trapped water volume
let mut prev_height = 0; // The previous height processed
// Process cells in increasing order of height
for (i, (h, r, c)) in cells.into_iter().enumerate() {
// Calculate the trapped water when the height increases
if h > prev_height {
// Calculate the number of inner cells not connected to the boundary
let boundary_size = ds.component_size(boundary);
let inner_cells = (i + 1 - boundary_size) as i32;
// Add the trapped water for the height difference
volume += (h - prev_height) * inner_cells;
prev_height = h;
}
// Union the current cell with its valid neighbors of equal or lower height
for &(dr, dc) in &Self::directions {
if let Some((nr, nc)) = to_valid_cell(r as i32 + dr, c as i32 + dc) {
if height_map[nr][nc] <= h {
ds.union(cell_index(r, c), cell_index(nr, nc));
}
}
}
// If the current cell is on the boundary, connect it to the boundary node
if is_boundary_cell(r, c) {
ds.union(boundary, cell_index(r, c));
}
}
volume
}
}
impl DisjointSet {
// Initialize a new disjoint set with `n` elements
fn new(n: usize) -> Self {
let parent = (0..n).collect(); // Each element is its own parent
let size = vec![1; n]; // Each set initially has a size of 1
Self { parent, size }
}
// Find the representative (root) of the set containing `v`
// and apply path compression for optimization
fn find(&mut self, v: usize) -> usize {
if self.parent[v] != v {
self.parent[v] = self.find(self.parent[v]);
}
self.parent[v]
}
// Union the sets containing `a` and `b`, attaching the smaller set under the larger set
fn union(&mut self, a: usize, b: usize) {
let root_a = self.find(a);
let root_b = self.find(b);
if root_a != root_b {
if self.size[root_a] < self.size[root_b] {
self.parent[root_a] = root_b;
self.size[root_b] += self.size[root_a];
} else {
self.parent[root_b] = root_a;
self.size[root_a] += self.size[root_b];
}
}
}
// Get the size of the set containing `v`
fn component_size(&mut self, v: usize) -> usize {
let root = self.find(v);
self.size[root]
}
}
Tags: #rust #algorithms #3d #sets